Progressive Scan vs Interlaced Scan: Key Differences
Discover the difference between progressive scan vs interlaced scan video formats, their impact on image quality, and their usage in modern and traditional.

Video broadcasting has seen an evolution from analog to digital formats. About 90% of companies use videos to boost their marketing worldwide. This evolution can only be possible because of advancements in technology, robust broadcasting platform support, and enhanced video streaming platforms.
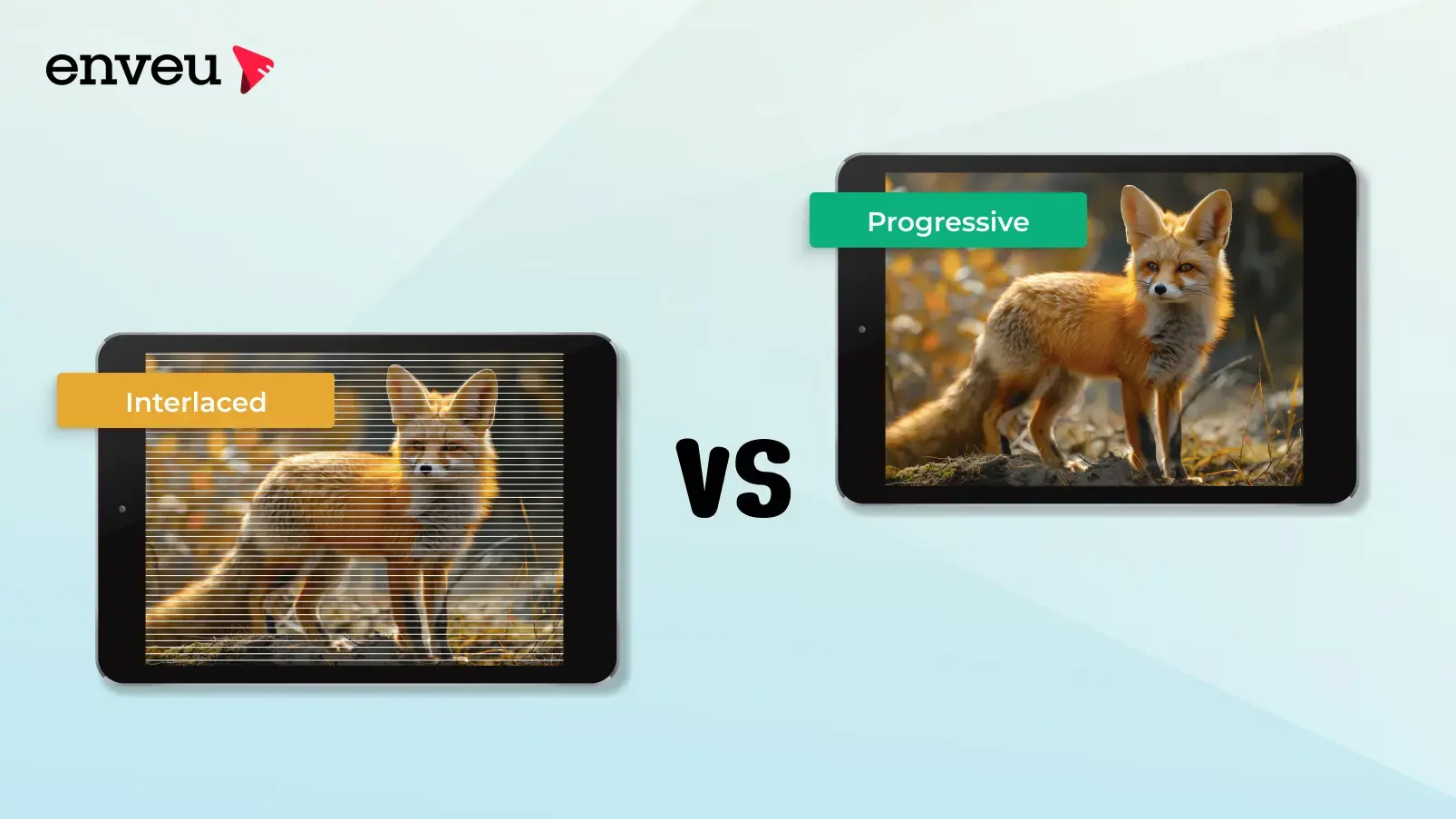
If we unfold the early days of video content, analog broadcasting used interlaced scan technology, where the frame was split into two field displays. This method was used to reduce flicker and bandwidth requirements. With time, the demand for digital broadcasting and flat-panel display increased, which made progressive scanning a superior technology.
Looking into recent statistics, it is evident that progressive scan formats have gained popularity over 70% by the global broadcast. Progressive scan completes the entire display in one frame and also enhances the viewing experience.
However, certain companies still prefer interlaced scans. To understand which is better, progressive scan vs interlaced scan, it is important to learn more about each of them and the comparisons between the two.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Progressive Scan?
Progressive scan is a method where each frame of video is displayed entirely in a single pass. It is one of the most used video production and display technologies. In this process, the frame is divided into two fields, one odd and the other even lines, where the display is done alternatively in successive passes. It is popular because of the demand for digital media and high-definition display support.
Advantages of Progressive Scan
- Reduced flicker: Interlaced scan exhibits flickering during fast-motion scenes, which is not the case with progressive scan. It provides a flicker-free and stable viewing experience, which makes gaming and watching sports and action movies easy.
- Better image quality: Progressive scan displays each frame fully, which makes images sharper and more detailed.
- Compatibility: LCD and OLED display screens have high compatibility with progressive scan as they have flat-panel displays. The scan here maximises the display capabilities and increases optimal viewing experience.
- Easy edit: This scan makes the post-production and video editing process easy as every visual information is in its respective frame. Video editors can apply effects and render without any complexity.
- Seamless digital distribution: For online content streaming and distribution, progressive scan formats are preferred because of their ability to maintain quality across various streaming resolutions.
- Future-proof technology: As the viewing expectations of the viewer are enhanced, progressive scan remains more adaptable as future-proof compared to interlaced scan. It works with current and emerging digital standards and therefore is a more sustainable choice for long-term use in broadcasting.
- Consistent quality: Progressive scan maintains consistent image quality across a wide range of content types. Be it a static image or a fast-moving scene, the viewing experience is enjoyable.
Disadvantages of Progressive Scan
- Higher bandwidth: Progressive scan requires higher bandwidth compared to interlaced scan to deliver video content at higher resolutions. This can be a challenge to some broadcasting and streaming applications having limited bandwidth availability.
- Compatibility issue: Older broadcast standards and equipment cannot rely on progressive scan. In this process, the content gets converted or downscaled for compatibility with the legacy system, which adds complexity and cost to the workflow.
- Processing power: More computational power and resources are required to process and render progressive scan video content.
- Motion blur: Sometimes, progressive scans exhibit motion blur in fast-paced action scenes and sports. The quality depends on the display refresh rate and response time.
- Short battery life: Devices using progressive scan experience shorter battery life as the processing power and energy consumption rate are huge.
What Is Interlaced Scan?
Interlaced scan divides each frame of video into odd and even lines. These lines will be displayed alternately in successive passes. Interlaced scans were originally developed for analog television and CRT (cathode ray tube) displays intending to reduce flicker time and conserve bandwidth.
Interlaced scan follows the process of display by first scanning all the odd lines of the image and then the even lines in the subsequent passes. This alternating method reduced flicker on early CRT televisions.
Advantages of Interlaced Scan
- Reduced bandwidth: Interlaced scan needs less bandwidth when compared to progressive scan. It transmits and displays only half the image in each pass. This makes the process efficient and has been ideal for early analog television broadcast and legacy transmission systems.
- Legacy compatibility: It is compatible with older CRT televisions, analog video equipment, and some broadcast standards which are designed around interlaced technology. It gives continued support to existing infrastructure and devices.
- Motion fluidity: As interlaced scan uses an alternating field display method, a smoother motion is offered to fast-paced action and sports video. The viewer experience is enhanced, especially on older displays.
- Data transmission: These scans can optimize the data and make it efficient for a smooth transition from analog to digital broadcasting.
- Suitability: Most of the historic and current broadcast companies developed from the analog era still use interlaced scan technology because of the high quality and reduced bandwidth requirements.
- Widespread adoption: It has been accepted by historical television broadcasters globally and are still picked by historical companies without any question.
- Lower processing demands: The scan requires less processing power and computational resources. This makes the process more suitable for real-time applications and live broadcasts.
- Cost-effective: It is more cost-effective to implement in consumer electronics and broadcast equipment, making it practical for mass-market adoption.
Disadvantages of Interlaced Scan
- Flicker: Interlaced scan has visible flicker, especially on larger screens and high-definition displays. It is caused because of the rapid alternation between odd and even lines.
- Reduced resolution: Due to the rapid alternation between the lines, the overall image quality and viewer comfort is compromised. It offers lower resolution and sometimes can be unfit for modern digital displays.
- Compatibility issue: Modern digital displays like LCD, LED and OLED screens are optimized for progressive scans. For interlaced scans, additional processing or deinterlacing techniques are required.
- Limited application: As the industry is shifting towards higher resolution (e.g., 1080p, 4K), the need to improve video standards is compulsory. Interlaced scans cannot inherit higher resolution capabilities. It restricts its usage to primarily legacy systems and specific niche applications.
- Motion artefacts: The alternating field display method of interlaced scan can produce visible artefacts and jagged edges of fast-moving objects. These artefacts can detract overall viewing experience and compromise the quality.
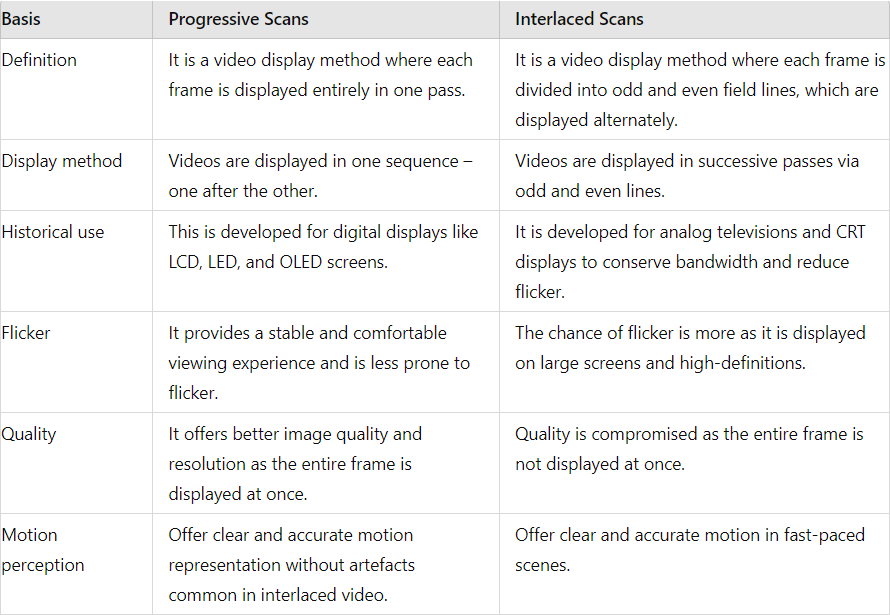
Difference Between Progressive Scan vs Interlaced Scans

Conclusion
The choice between progressive scan vs interlaced scan depends entirely on the specific broadcasting requirement and technological consideration of a company. Progressive scan is generally picked as it can deliver high-definition, superior-quality image and evergreen broadcasting environments. However, interlaced scan holds relevance too to certain scenarios, as mentioned above.
There are other options available as well for broadcasters today to smoothen their content delivery and optimization. Enveu is a platform companies can look into without any question as it is tailored to cater to modern broadcasting needs. Whether the company is transitioning to progressive scan formats or interlaced content, Enveu has the tools and expertise to enhance content quality and keep up with the viewer’s satisfaction.
By choosing Enveu for your broadcasting solution over OTT, businesses can stay ahead in this fastest-growing digital media delivery.